Publish date: 8.26.24
During estrus synchronization, the three most used hormones are gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), prostaglandin F2α (PG), and progesterone. Each of these drugs has a very specific purpose during estrus synchronization, therefore, it is critical that they get administered on the correct day of the estrus synchronization protocol. Let’s learn more about these hormones and the corresponding products in the marketplace.
GnRH
GnRH is used during estrus synchronization to stimulate the ovulation of a follicle and the formation of a new follicular wave. When GnRH is administered at the beginning or middle of a protocol, it is used to stimulate the ovulation of a follicle, so a new, synchronized follicular wave can begin. Giving GnRH at the time of artificial insemination (AI) stimulates ovulation, so an egg can be released to become fertilized by the deposited sperm cells. If GnRH is accidentally administered instead of PG at CIDR removal, the females that respond to it will not have an egg available for fertilization at the appropriate time for AI.
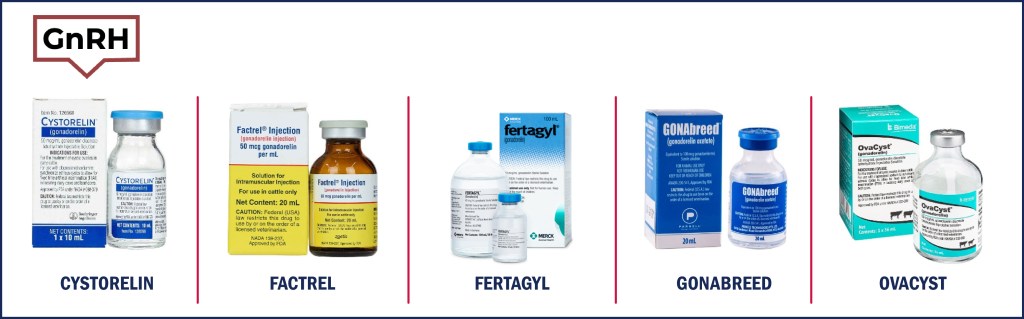
There are currently 5 GnRH products on the market: Cystorelin, Factrel, Fertagyl, GONABreed, and OvaCyst. All these products are administered in 2 mL doses except for GONABreed, which is administered in a 1 mL dose. These GnRH products need to be administered intramuscularly, so make sure that you are using the correct needle length (1.5 inches).
Ensure you read the label and store GnRH products under the correct conditions, as some need to be refrigerated and others stored at room temperature. Below are images of all the GnRH products.
Progesterone
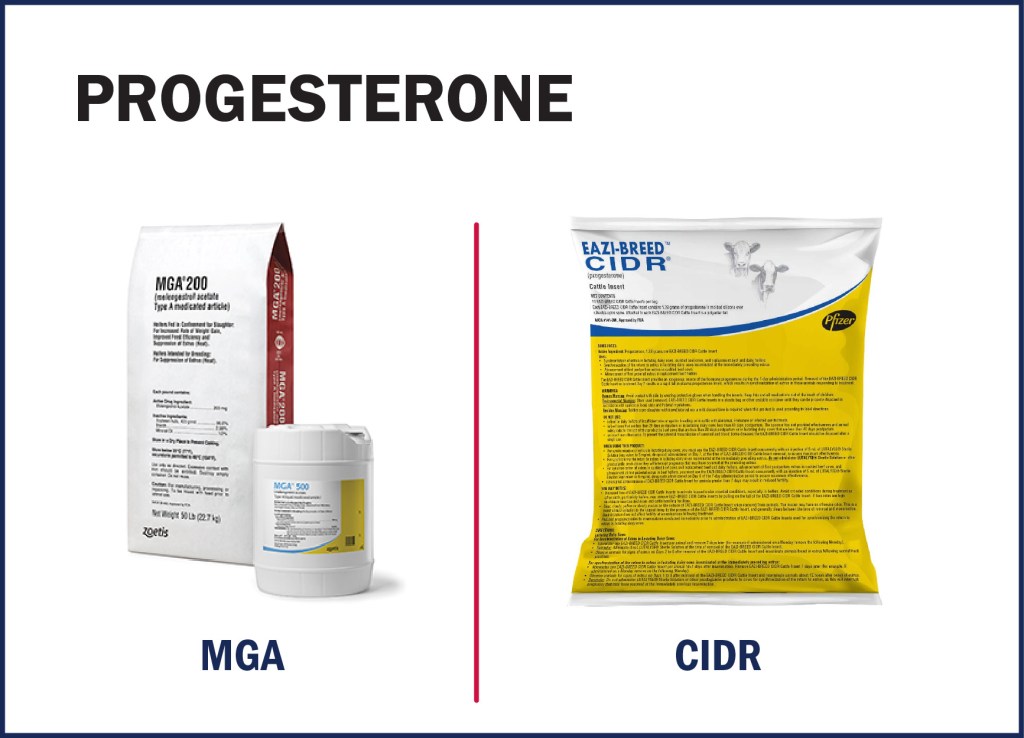
Progesterone is administered as a controlled internal drug release (CIDR) insert or is fed as melengestrol acetate (MGA) at a rate of 0.5 mg/head/day. During the estrus cycle, the corpus luteum forms at the sight of a ruptured follicle and will begin to release progesterone. Due to the elevated concentrations of progesterone, the female will not come into heat and will not ovulate.
In the context of estrus synchronization, we use exogenous progesterone (via a CIDR or MGA) to mimic the effect of the corpus luteum and inhibit females from coming into heat before the desired time. Once we remove the CIDR insert or stop feeding MGA, concentrations of progesterone will drop, and the female will be able to come into heat.
The use of progesterone is recommended during estrus synchronization of cows and heifers as it can help kick-start cyclicity in non-cycling females. The images below show you what to look for in terms of CIDRs and MGA.
Prostaglandin F2α (PG)
Prostaglandin F2α is used to break down a corpus luteum that may be present on the ovary. When a corpus luteum is present, it produces progesterone, which inhibits a female from coming into heat and ovulating. Therefore, by administering PG a few days prior to AI, we can break the corpus luteum down and reduce circulating concentrations of progesterone. This allows the female to come into heat and ovulate.
If PG is accidentally administered in place of GnRH at the start of a protocol, a new follicular wave will not be initiated in a synchronized manner and a suitable follicle may not be present at AI. If PG is administered instead of GnRH at AI, there likely won’t be a corpus luteum for it to respond to and certain females may not ovulate spontaneously in time to be fertilized by the sperm cells deposited.
There are currently 6 PG products on the market: estroPLAN, Estrumate, Lutalyse, Lutalyse HighCon, ProstaMate, and SYNCHSURE. Lutalyse and ProstaMate are administered in 5 mL doses, whereas the other products are administered in 2 mL doses.
These PG products are administered intramuscularly, except for Lutalyse HighCon, which can be administered either intramuscularly or subcutaneously. Again, it is very important to read the drug label and store your PG under the correct conditions.
If pregnant cows or heifers are injected with PG, they may abort, depending on the stage of gestation. Therefore, only administer PG to non-pregnant females. See the images below to know which products are Prostaglandin F2α.

Estrus synchronization requires time, effort, and financial investment, so ensure success by:
- Sticking to the estrus synchronization protocols recommended by the Beef Reproduction Task Force
- Administering the correct drug on the correct day
- Using the correct needle length for the intended route of administration (1 inch for subcutaneous administration and 1.5 inch for intramuscular)
- Storing your estrus synchronization hormones under the conditions recommended by the manufacturer
Start implementing a synchronization program in your herd by contacting your ABS Representative or completing the form below.






